Tipos de ronchas en la piel fotos refers to types of hives on the skin photos. Ever experienced an acute, extremely itchy skin eruption that appears quite abruptly and seemingly out of the blue? It may be hives on you. Also known as urticaria, this common disorder manifests itself through elevated red or skin-colored welts that may be disturbing. Though usually temporary, hives may indicate another problem. This booklet will take you through the various strains of hives, along with causes and symptoms, to give you a better idea of what could be going on with your skin.
What Are Hives?
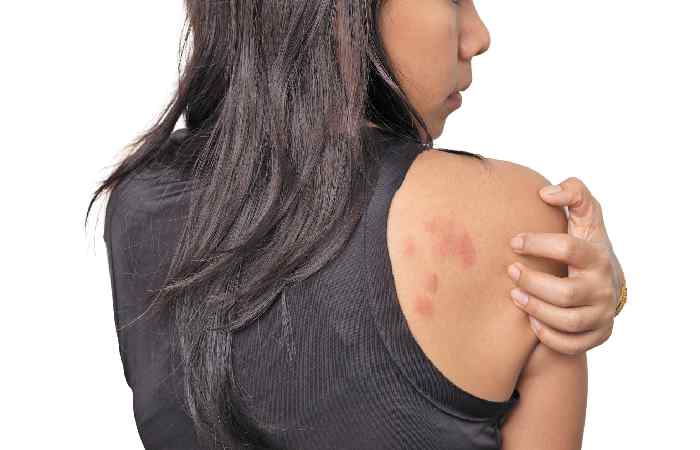

The swelling of the skin during further hives is understood as pale, fast red bumps (or plaques (wheals) on the skin surface, emerging immediately. They usually represent a response to an incitement by the immune system of the body. This reaction usually brings upon hives and can be an allergic response.
The first step involved in managing and treating the various types of hives is to understand them. Although most of the cases are resolved minutely, some may become repetitive. To have a clear understanding of these, we will expound on the following classifications.
How Hives Form on the Skin?
The onset of an outbreak of hives is initiated by the activation of the immune cells in your body (mast cells). These cells, in turn, produce chemicals such as histamine in your blood.
This chemical discharge causes small blood vessels under the skin to widen and seep fluid. It accumulates in pools just below the surface of the skin and creates the bumps of the swollen hives. This process may be triggered by a variety of factors.
Common triggers that stimulate this reaction include:
- A food, drug, or insect sting allergic reaction.
- Physical agents like scratching or pressure, or very hot temperatures.
- Unnoted infection or disease.
Tipos De Ronchas En La Piel Fotos – Identifying the Symptoms of Hives
The diagnosis of hives is usually easy because they have a characteristic look. Raised, itchy bumps are considered the most common symptoms of hives and may be red or skin-colored. This rash on the skin may be present in any part of the body and may appear to travel around the body since the old welts disappear and new ones appear.
A single hives episode may appear irregular and differently shaped as well as different sizes, and might run together into bigger areas. The initial step in distinguishing between hives and other skin conditions is whether you know what to be on the lookout for.
Typical Appearance and Sensations
The characteristic appearance of hives is familiar to you after you learn the symptoms. The urticaria type of rash manifests as welts, or more commonly known as the wheals, on the skin. There are a number of common features between these welts.
You can often identify hives by looking for:
- Red or skin colored raised bumps that itch.
- Well-defined sides to all the welts.
- Blanching and pressing the centre of a red hive, where the white appears.
- The differences in structure and size can be dots or huge patches that connect.
The main effect, other than the appearance, is the itching that is either mild or severe. There is also a burning or stinging sensation, which is reported by some people. The harshness of symptoms may vary, and personal warts commonly go away in 24 hours.
Main Types of Hives on the Skin
In order to treat hives correctly, it is beneficial to be aware of what type you are allergic to. The major categories of hives are categorised according to duration. There are two major classifications: acute urticaria and chronic urticaria.
Hives can also be acute (short-lived) and chronic (long-term, untreatable disease). In other cases, chronic hives can manifest themselves without some precipitating factor, a situation called chronic spontaneous urticaria. These classifications will be discussed in the following sections in more detail.
Acute Vs. Chronic Hives
The main way acute and chronic hives differ is by duration. The acute hives are identified as outbreaks lasting less than six weeks. In many cases, hives have a specific and determinable cause, and often one episode of hives attacks may be prompted by the usual things like food allergy, an infection, or a medication reaction. Acute hives tend to clear up by themselves.
Chronic hives, in turn, are even more chronic, as they can persist longer than six weeks and recur every day or near-daily as well. Such a chronic disorder might be more complicated to control since a trigger is not always apparent.
The cause is unknown when chronic hives is unknown and is thus known as chronic idiopathic urticaria. The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology explains that such hives generally do not leave bruises or scars, but they may be quite itchy and disruptive [1].
Allergic and Environmental Hives
Most of the hives can be definitively traced back to external factors, either due to an allergic reaction or in the environment. The common triggers that can cause an instant outbreak of itchy welts would include a food allergy or insect bites. It means that your body is virtually ringing the bell that it has experienced something that it does not like.
Other than allergies, hives can also be spurred by certain environmental conditions. These non-allergenic causative agents are equally vital to determine.
Hives Caused by Allergies
One of the most common causes of the hives is an allergic reaction. This happens when your body is not in tune with the response your body gives to a normally inoffensive substance. Typical aggravators are some foods such as peanuts, eggs, nuts, and shellfish. Drugs, and especially antibiotics such as penicillin, are also common offenders.
Allergy to insect bites, stings, exposure to dander (specifically pet dander), pollen, and latex can also be other allergens. The arrival of the hives is normally soon after you have touched the allergen. This is due to an allergic reaction whereby your body secretes histamine, which causes the typical itchy welts we know.
When an allergic reaction leads to hives, it is imperative that one monitors such cases to ensure that the reactions are not getting worse. Having hives in combination with the swelling of the lips/tongue, or shortness of breath may be an indication of the development of anaphylaxis. These anaphylaxis symptoms are symptoms of a severe allergic reaction that needs emergency care.
Environmental Factors—Temperature, Sunlight, and Pollution
Lockets, location, and surroundings may be a significant factor in physical urticaria. The alteration in your body temperature is one of the most common causes. As an example, exercise, hot showers, or anxiety may increase a person’s core body temperature, resulting in a case of cholinergic urticaria that presents as small and intensely itchy hives.
On the other hand, cold urticaria may develop because of exposure to cold. This is a response that occurs when you undergo exposure to cold air or cold water, and subsequently, your skin warms up. Light is another environmental factor that may trigger solar urticaria even when a person is surrounded by the sun for a few minutes.
Though not so explicitly associated, other environmental factors are thought to be causes of hives.
These may be:
- Airborne pollutants
- On the skin, there is water on rare occasions
- UV rays of tanning beds
Unique Forms of Physical Hives
Although physical urticaria is usually evoked by temperature and sunshine, there are other distinct varieties of hives. Direct physical stimuli also trigger these forms, and their symptoms may happen in the form of hives that may be equally disruptive. These less apparent triggers are important to be identified by any individual who has frequent outbreaks without knowing the cause.
Knowledge about these particular types of physical hives can assist you in identifying what is causing you the discomfort and preventing it.
Conclusion
Tipos De Ronchas En La Piel Fotos – In a nutshell, it is important that one gets to understand the types of hives on the skin so that he or she may effectively manage and treat them. As there are acute and chronic hives and hives resulting from physical factors (such as pressure or a temperature change), it is possible to identify those and be more effective in treating the symptoms. Allergic reactions and natural interactions/environment also influence the development of hives; therefore, it is important to detect possible allergens and irritants within your environment.