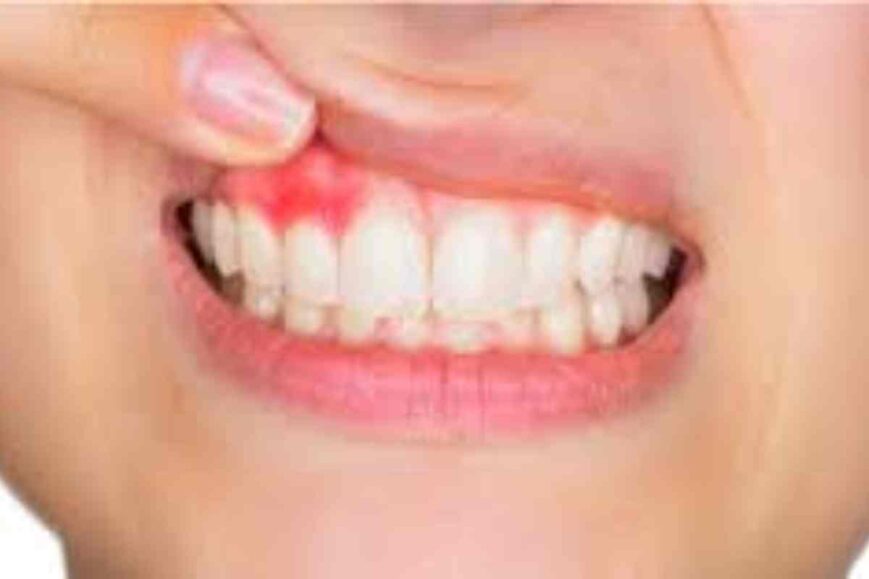
Pictures of Gum Boils – Gum boils are deposits of pus in the gum area inside the mouth of a person. If left untreated, gum boils also known as gum abscess can cause serious problems, but knowing about it early and treating it can help you feel better.
Gum Boils or Gum Abscess
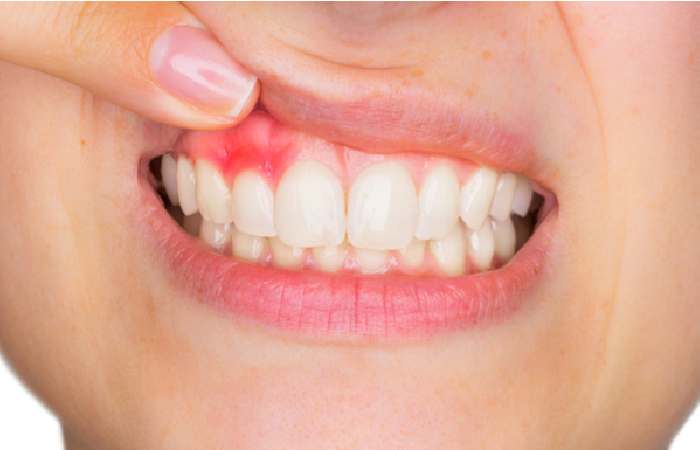
A gum abscess is the collection of pus in many parts of the body including the mouth. An abscess is a pus-filled pocket that can appear in many parts of the body, including the mouth. Some people develop toothaches that affect the area where the teeth are located.
Nevertheless, occasionally there develop abscesses in gums. The symptoms of a gum abscess should be observed, and it should be treated in case it occurs.
What are the causes of Gum Abscesses?
The gum disease is an infected space which is attributed to bacteria in the mouth. Poor oral hygiene causes periodontitis, which in turn causes some gum disease. Plaque is a racist film of bacteria which is sticky and is colorless. Unless it is taken out of the teeth with the help of brushing and flossing, the tissues that surround it can get infected. This can lead to an abscess
Long-term deposits of bacteria can also lead to gum abscesses. Periodontal pockets are areas that form around the teeth due to the gum tissue. Bacteria can live in this environment. If food and plaque get into this area, the bacteria can multiply.
The immune system is weak and hence can result to gum disease. Factors that may reduce your immunity are fatigue, stress or chronic diseases.
Symptoms of a gum abscess
A few oral diseases of the mouth and gums are not visible by naked eyes and may lead to certain initial symptoms. The same cannot be said of gum abscesses. Upon opening the mouth and scrutinizing the area you determine that it is swollen and reddish. Additional indications of gum disease are
- Resistance to hot or cold foods and drinks
- Pain when chewing
- Loose teeth
- A bad feeling in the mouth (due to pus discharge)
- Pus
- Fever
How to diagnose a gum abscess?
When you feel pain, you have gums tendencies and bad breath you should not disregard those symptoms. Speak to your dentist early enough. On the basis of your symptoms, your dentist can lead to the diagnosis of gum disease (or carry out other tests). These hungerhood, swelling, and redness.
Besides checking your gums, your doctor can also order dental X-rays to check whether there is a disease or dental disease (an infection in the body). Your doctor can also use X-rays to determine whether or not there is a loss in your bones because of disease. But you must go to your dentist even after the abscess pops and empties, to deal with the infection.
How does a gum abscess get treated?
The gum abscess cannot be self-treatable and therefore, it is important to seek the help of a dentist to cure. Gum abscesses are treated with drainage of abscess as well as scraping of periodontal pockets. Deep cleaning can be suggested by your dentist, so-called scaling and root planing. This is a process that cleans off the plaque and tartar between and down the gums. This is a surgery that comes in the form of an incision over the abscess. To begin with, your dentist can use a local anesthetic.
X-rays will help your doctor to know whether your gums are damaging bone. Toy your dentist might also extract the tooth depending on the level of bone damage. They can also prescribe a way of reconstructing lost bones or gums.
This tissue comprises blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. In case the tooth has in its pulp, root canal may be required to restore the damage to the tooth.
Medicines
In addition to these dental procedures to eliminate and treat the infection, your dentist may also prescribe antibiotics.
When your dentist is unable to eliminate the abscess, antibiotics should be used so as to curb the swelling. These medicines also aid in preventing recurrence and prevent the growth of the infection to other body parts.
In case you are ill your dentist can prescribe you antibiotics. Warm salt water gargles or over-the-counter pain reliever (for example ibuprofen) will help the patient feel better and less painful before they visit the dentist.
Complications of a gum abscess.
Do not ignore gum abscesses. The infection has the potential to spread deep to the gums and also on to teeth and bones when not treated. It will be painful and swollen, and the infection will be absorbed into other organs and bodies. to sepsis. Symptoms of sepsis include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Abdominal pain
- Rapid heartbeat
- Fever over 38°C (101°F)
How to prevent a gum abscess?
Look after your mouth to avoid the gum disease. This would be through brushing and rinsing the teeth on a regular basis. Wash your teeth twice or thrice day especially after food. This lowers the amount of the plaque around your teeth as well as under your gums.
Furthermore, clean your teeth at least one time in a day and remove food and plaque in your mouth. Clean your teeth on a social basis after each six months. Having the ability to monitor the well-being of your teeth and gums, your dentist is in a position to notice any issues in your oral cavity early on and prevent any illness or infection.
Canker sore on tongue: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention.
A cultural sore in the tongue is highly painful and it hurts to perform normal tasks like eating, imbibing beverages, speaking among others. Not very serious mouth ulcers these are, and are not unusual, but can create a complication in normal life. The knowledge of what causes the formation of canker sores on the tongue, the treatment of the disease, and the ways of preventing the occurrence of further outbreaks would help you better cope with the sickness.
It is by means of this elaborate manual that you will learn everything that you need to know about canker sores on the tongue, and that in a simple and straightforward manner.
What Is a Canker Sore on the Tongue?
A canker sore also called aphthous ulcer is a tiny deep lesion that is located in the mouth. It can be worse when it appears on the tongue since it is usually painful than the sores that appear on the cheeks or lips since the tongue catches in every movement.
Canker sores are not contagious as opposed to cold sores. They tend to be round or oval white, yellow, or gray spots with a red halo, with some staying up to 14 days.
Common Causes of Canker Sores on the Tongue
Canker sores can develop for many reasons, and often more than one factor is involved.
Minor Injuries
-
Accidentally biting your tongue
-
Burns from hot food or drinks
-
Irritation from braces, dentures, or sharp teeth
Nutritional Deficiencies
- Low levels of vitamin B12
- Lack of folic acid or zinc
- Iron deficiency
Stress and Hormonal Changes
- Emotional stress or anxiety
- Hormonal fluctuations, especially during menstruation
Food Sensitivities
-
Salty or rough-textured foods
-
Acidic foods like citrus fruits and tomatoes
-
Spicy foods
Weakened Immune System
-
Illness
-
Fatigue
-
Certain medications
Symptoms of a Canker Sore on the Tongue
A canker sore on the tongue often causes noticeable discomfort. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in tongue which is sharp or burning.
- A white or yellow spot having a red functional area.
- More pain with taking food or oral talking.
- This is preceded by tingling or burning sensation before the sore.
- The peri-affected swelling.
In severe cases, multiple sores may appear at once, making it difficult to eat properly.
Types of Canker Sores That Affect the Tongue
Canker sores are generally classified into three types:
| Type | Size | Healing Time | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minor | Small (less than 1 cm) | 7–10 days | Mild |
| Major | Larger and deeper | 2–6 weeks | Painful |
| Herpetiform | Multiple tiny sores | 1–2 weeks | Moderate to severe |
How to Treat a Canker Sore on the Tongue
Most canker sores heal on their own, but treatment can help reduce pain and speed recovery.
Home Remedies
- Saltwater Rinse: This one is useful in reducing bacteria and swelling.
- Honey use: Natural healing, antimicrobial, and remedial.
- Coconut oil: Could help lessen irritation and help to heal the wound.
- Ice chips: Desensitise and relieve suffering.
Over-the-Counter Options
- Painkillers in oral forms of gel or paste.
- Antiseptic mouthwashes
- Protective oral patches
Medical Treatment
If sores are severe or recurrent, a doctor may prescribe:
-
Corticosteroid gels
-
Prescription mouth rinses
-
Supplements if deficiencies are found
Foods to Eat and Avoid with a Canker Sore on the Tongue
Diet plays a big role in managing pain and healing.
Recommended Foods
| Food Type | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Soft foods | Yogurt, mashed potatoes | Easy to chew |
| Cooling foods | Smoothies, cold milk | Reduce irritation |
| Nutrient-rich | Eggs, leafy greens | Support healing |
Foods to Avoid
| Food Type | Examples | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Spicy foods | Chili, hot sauces | Increases pain |
| Acidic foods | Citrus fruits | Delays healing |
| Crunchy foods | Chips, nuts | Can reopen the sore |
How Long Does a Canker Sore on the Tongue Last?
Canker sores on the tongue resolve in one or two weeks and have no scars. Bigger or repeated sores can be long-lasting and must be considered by a health practitioner in case they do not get better after 14 days.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical advice if:
-
The sore lasts more than two weeks
-
Pain is severe and worsening
-
You experience frequent outbreaks
-
You have fever or difficulty swallowing
These may indicate an underlying health issue that needs attention.
Tips to Prevent Canker Sores on the Tongue
| Prevention Tip | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Maintain oral hygiene | Reduces bacteria |
| Use a soft toothbrush | Prevents tongue injury |
| Manage stress | Reduces outbreaks |
| Avoid trigger foods | Lowers irritation |
| Eat a balanced diet | Prevents deficiencies |
Final Words
A tongue sore may be small but the pain due to it may be unbearable. The good thing is that most of them are mild and acute. Through using the triggers, maintenance of mouth hygiene and simple management, you will be in a position to cure pain and prevent future exposure.
In case canker sores continue to recur or disrupt a normal lifestyle, the next best thing is to visit a health practitioner. When proper treatment is applied, recuperation is only a few days off.